Photogrammetry Vs Orthophotography - What’s The Difference?
Facing photogrammetry vs orthophotography is a way to see the differences and similarities these technologies have in order to decide which is best. Photogrammetry is a technology commonly used to create 3D models from a series of photographs, while orthophotography makes reference to overhead imagery that have been rectified to a uniform scale.
To better understand these two technologies and decide which is best, we break them down into details here below.
Photogrammetry and Orthophotography Explained
As we promised above, we are going to fully explain the nuances of photogrammetry vs orthophotography. And we are going to do so by starting with the first one.
Although it may sound as a brand-new technology, photogrammetry has been around since the 19th century, the same moment when photography was invented. However, it was not until recently that it has become a more accessible and versatile technology.
The basic principle of photogrammetry is to collect information from photographs taken at different angles of the same object and its environment. Then, the software uses the information and properly aligns the photographs to calculate the location of relevant points and the distances between those points in a 3D space. Finally, it uses the results of the calculations to generate a polygonal mesh that will serve for the creation of the 3D model.
In a similar way, the working principle of orthophotography is based on photographs, but the main difference is that they are taken from the air, generally by means of a drone or an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV). These photographs are geometrically corrected to represent a uniform scale to facilitate the possibility of measuring aspects such as distances between buildings, streets and other parameters that may be relevant for the specific application.
From the descriptions given above, it is easy to see that the main difference between photogrammetry and orthophotography is that orthography leads to 2D map-like results, while photogrammetry converts flat images into a 3D result. In other words, these technologies use the same input, but provide different outputs.
Moreover, anyone could say that photogrammetry covers orthophotography, since it can be used to process aerial photographs to create special representations such as topographic maps.
There are three different types of photogrammetry:
- Manual photogrammetry – although it can be focused on the specific points required, it is usually the slowest and less accurate method.
- Target photogrammetry – an automatic method where higher accuracy is obtained, but it requires more time to set it up.
- Dense matching photogrammetry – the most similar to standard 3D scanning, since it generates a dense cloud of mesh points.
At this point, you might have other questions about photogrammetry and orthophotography, such as what are their applications? Or what do you need to apply each technology? No need to worry, just keep reading as we give you the answers.
What are the main characteristics of photogrammetry?
- It can generate 2D or 3D digital models.
- It uses methods from different disciplines, such as optics and projective geometry.
- It can also use video as the input.
- It requires high computing power to process the images.
- It can be used as an alternative to 3D laser scanners.
What equipment is necessary for photogrammetry?

- A camera. The higher the resolution the better.
- A tripod. Although it may not be necessary, it is recommended to ensure proper focus and less distortion.
- Photogrammetry software. Nowadays, you can even find free options. However, they may have a limited functionality when compared to premium software.
- A workstation or PC with the capacity of running the software properly.
What are the main applications of photogrammetry?
Thanks to the most recent developments in photogrammetry software, common cameras can now be used to model measure almost everything, including but not limited to:
- Buildings
- Auto parts
- Ships
- Pipeline installations
- Sculptures and other types of arts
- Crime scenes
- Film sets
- Topographic maps
- City plans
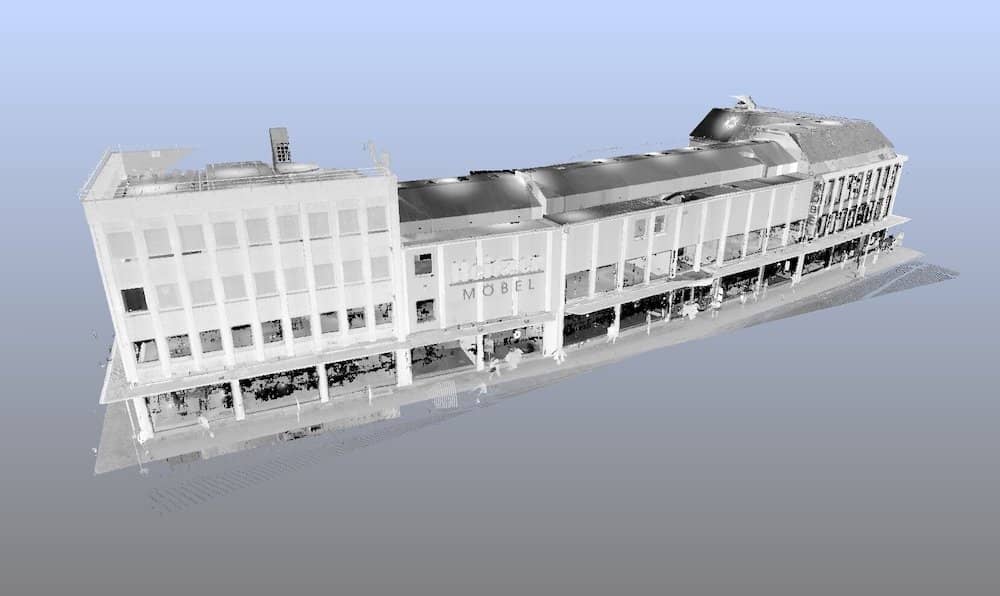

Obviously, many different sectors can benefit from photogrammetry. However, the most common sectors that apply photogrammetry are:
- Architecture and construction
- Automotive
- Energy
- Maritime
- Mass manufacturing
- Engineering services
What are the main characteristics of orthophotography?
- It generates a 2D map-like image.
- It performs image correction for topographic relief, camera tilt and lens distortion.
- Photographs used can be aerial or satellite taken.
- It uses Digital Elevation Models (DEM).
- It generates images with accurate uniform scales.
- It is possible to measure directly on the resulting image. Usually, other layers of data are applied to the orthophotograph.
- It is usually integrated with a Geographic Information System (GIS)
What equipment is necessary for orthophotography?
As you can imagine, the setup for applying orthophotography includes pieces of equipment that can also be found when applying photogrammetry. However, we show you the main differences in the following list:
- A specialized camera for drone or satellite image capturing
- Drones, aircrafts or satellites
- Image correction software
- A workstation or PC to run the software
It is important to highlight that different applications require different software programs.
What are the main applications of orthophotography?
Due to the nature of the images obtained with orthophotography, this technology is of special interest in applications that require information about the essence and use of the surfaces displayed. It also comes in handy for communication purposes. As the old saying goes, an image is worth a thousand words.
This said, a short list of the most relevant applications of orthophotography must include:
- Topographical representations (GIS)
- Creation of layouts for road, rail and waterway development and planning
- Creation of layouts for energy transportation
- Pipelines layouts
- Communication lines layouts
- Mapping areas in risk of flooding
- Creation of hydrographic and other similar maps
- Representations of environmental impact for environmental studies
- Status of areas affected by natural disasters
Clearly, the list shown above offers a great view of the many sectors that take advantage of using orthophotography. However, it is most frequently used in:
- City planning and urbanism
- Large agricultural projects
- Energy infrastructure projects
So, which is besT?
We have been discussing the details of photogrammetry and orthophotography until this point because we wanted to help you decide which is best.
However, this decision will mainly depend on the specific application you have in hand and the resources available for that application.
What is clear is that, if you have a small budget and your application involves modelling a simple 3D object, the obvious choice is using a simple photogrammetry setup. However, if you are going for a bigger project or need very high accuracy you may want to consider a professional photogrammetry or orthophotography service to guarantee expected results.
We offer professional photogrammetry and 3D scanning services for buildings, ships, pipeline installations and single parts that are used when applying reverse engineering. Our team is formed of trained and experienced professionals, and we only use top-notch technologies to guarantee high-quality and accurate results at very competitive prices.
Contact us
Whether you just have a small question or want to get a customized offer from us:
Contact us now.
We are happy to help you.
