What Is Laser Scanning Used For

Laser scanners are becoming one of the most important tools in a surveyor’s arsenal. The technology has become more sophisticated over the years. But what exactly is laser scanning anyway, and what is it used for?
Laser scanning is a method primarily used to collect measurements of a given object or area. The data collected is then uploaded to a cloud service so that it can be accessed later and translated into spatial data. That data is then used to construct a 3D model.
If you’d like to learn more about why surveyors use laser scanning, you’ve come to the right place. In the following sections, we’ll breakdown some of the technicalities surrounding laser scanning, as well as what types there are and what they can be used for beyond just land surveying.
What industries use laser scanning?
There are far more uses for laser scanners than we could possibly list here. We’ll present you just a few of the most interesting ways that laser scanners are used in the real world. Most of these examples involve land surveying, however, we think it’s important to point out that laser scanning is used in other disciplines such as manufacturing.
Laser scanning in land surveying

One of the most common and well known uses for laser scanning is land surveying. In the first half of the 20th century, land surveyors had to make their measurements with nothing but a partner, a chain/rope, and trigonometry to aid them. Today land surveyors use laser scanners to get far more accurate measurements and to centralize the data they discover.
Laser scanning in conservation

Laser scanning in manufacturing
Laser scanners can provide spatial data for more than just landscapes. In manufacturing, industrial 3D laser scanners are often used for prototyping, quality control, and even reverse engineering. For quality control, laser scanners can be used to ensure the dimensions of whatever the manufacturer is producing are exactly right. In the same token, they can use laser scanners to discover the exact dimensions of competitors’ products as you’ll see below.
Prototyping with laser scanning
The usual prototyping process without laser scanning involves multiple areas of expertise, expensive tools and a tedious time consuming process. With 3D laser scanning, on the other hand, manufacturers can expedite the prototyping phase by figuring out the complex dimensions of their products.
Manufacturers can then save all of the data about their products to the point cloud for retrieval later if they need it. This often happens in the event of a recall. When a recall comes up, having an exact 3D model of any given product will give the manufacturer a head start at identifying and fixing the cause of the problem.
Reverse engineering with laser scanning
If a rival company has a product and you want to know exactly how it is made and how it works, laser scanning can get to the bottom of it. Scanning can allow you to breakdown the dimensions and parts of a product much faster and with less hassle than measurements by hand. Manufacturers often employ this technique when they are trying to see how a competitor’s product works.
Surprisingly, manufacturers also use this on their own products. If there is a product they no longer make anymore but need to analyze for some reason, they have two options. They can scan one they still have lying around or pull up a scan they might have made when the product was still in production.
Of course, this has implications far beyond just manufacturing. Manufacturers are not the only ones who use this technique, as you will soon find out in our section on the military.
Quality control with laser scanning
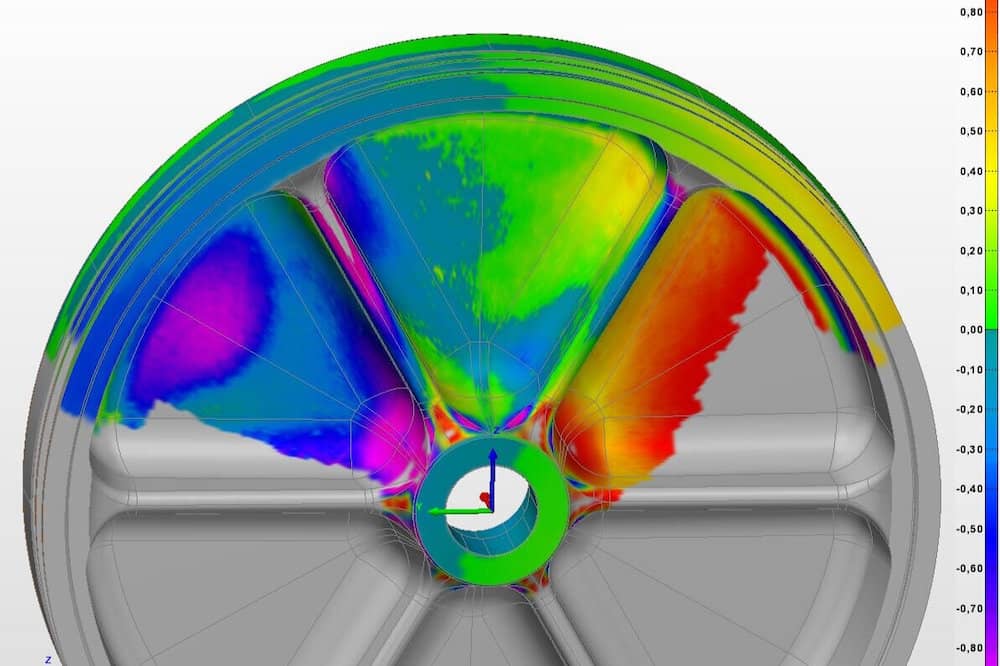
When objects are examined by hand for quality control, it can be very costly for a business and time consuming. That’s why so many businesses are turning to laser scanning for their quality control.
Laser scanning can improve quality control by:
- Taking accurate measurements without the fear of human error.
- Allowing businesses to save a file for every product they produce, which can be printed on a 3D printer. This allows for quick and easy replacements if need be.
- Comparing the designed model with the real model and allowing for a quick detection of problems.
- Saving the information it gathers to a cloud for ease of access.
Laser scanning in cave exploration
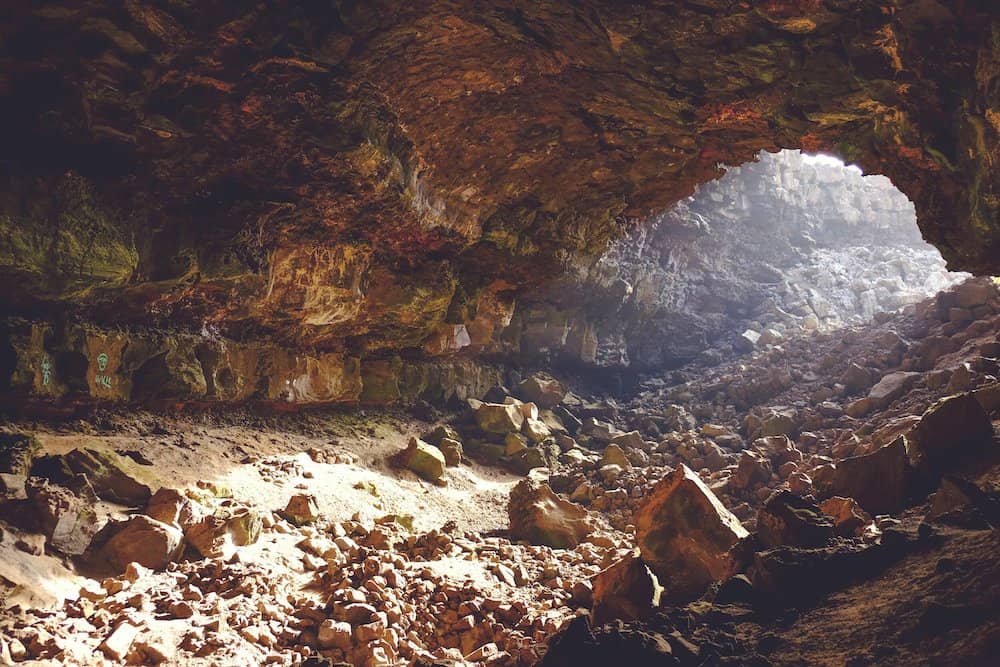

Laser scanners can make mapping out a cave far less stressful than it would otherwise be. Instead of trying to wiggle their way into dangerous tight spaces, scientists can use laser scanners to map out every nook and cranny of a cave. This also saves them time because of the versatility of the laser when compared to measuring distance by hand.
Laser scanning in archeology
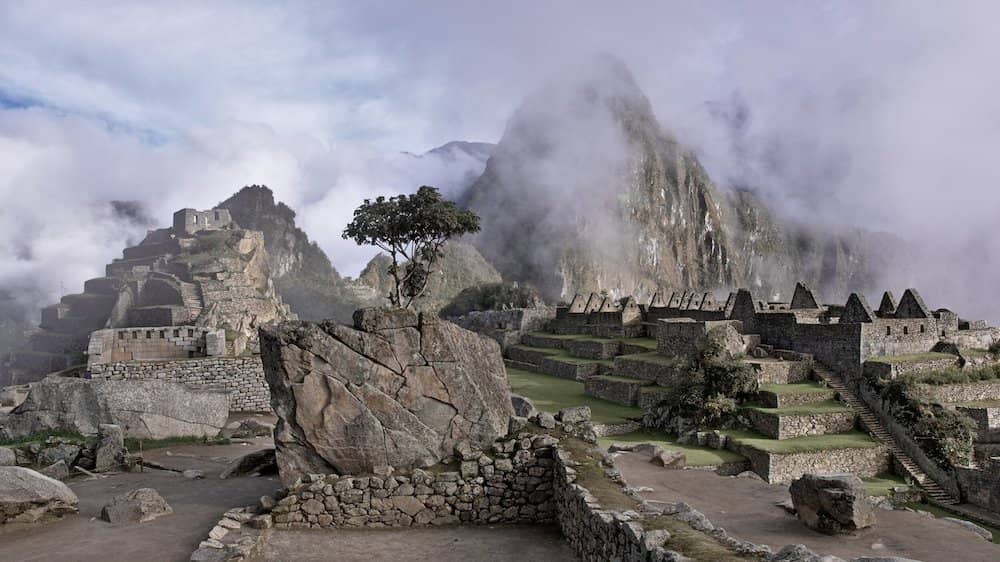

Archaeologists use laser scanners in order to explore areas that they may not be able to reach themselves. During the early part of the 2010’s, laser scanners were actually used to find a lost Mayan city. Laser scanning can not only help with new discoveries but it can be used to map out areas that are just too dangerous to enter, expanding what our archeologists are capable of studying.
Laser scanning in the military
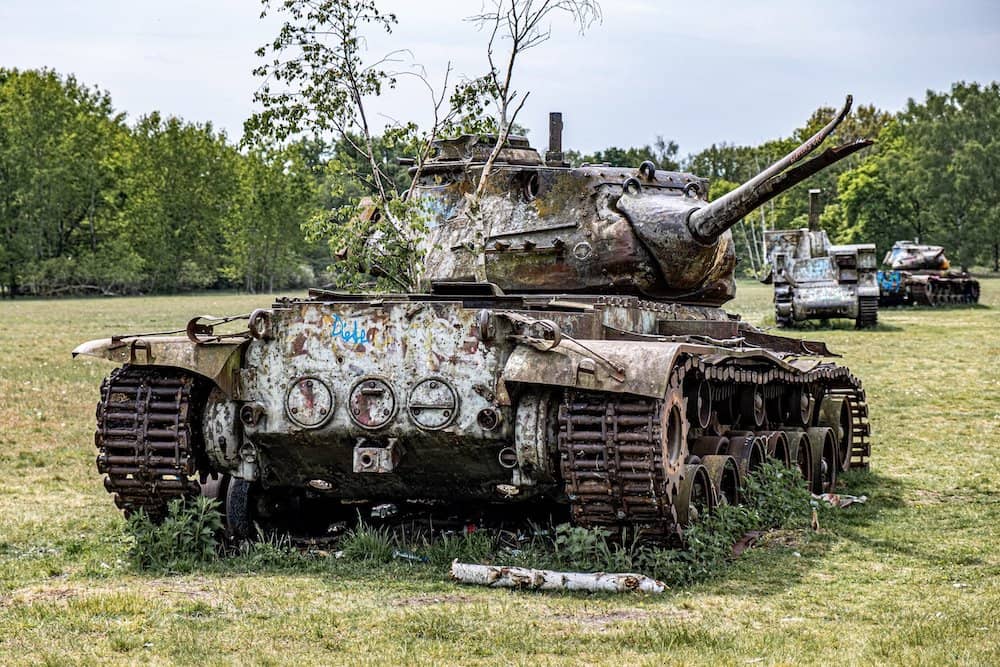

The military uses laser scanners to map out the inner workings of their equipment so that they can make exact replicas to act as spares. The reason they have to do this instead of just ordering new parts is because a lot of military equipment is old, and the companies that originally manufactured them no longer exist in many cases. They essentially scan the space inside the equipment the same way a land surveyor would scan the space in a given landscape.
Laser scanning on the highway
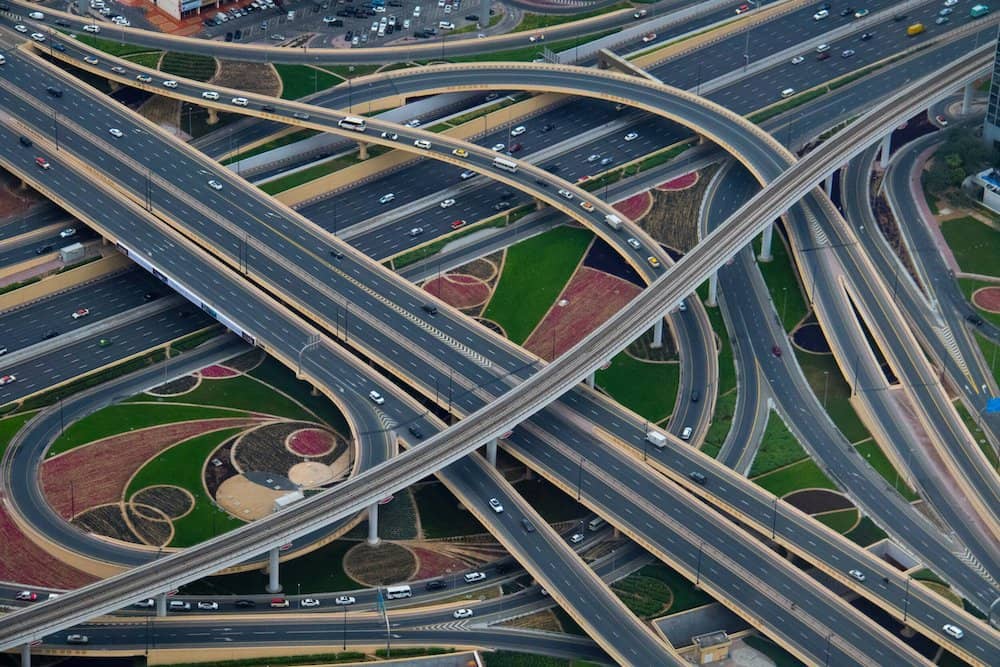

Figuring out the terrain for a construction project on the highway, comes with the added challenge of traffic. If you were trying to make these measurements the manual way, you’d have to close down the highway for a considerable amount of time. However, laser scanning can be done very quickly and may not even require shutting down the highway at all.
One example of this in practice is when investigators try to figure out what happened in a traffic accident based on the position of debris, marks left on the road and the eyewitness testimony. Investigators can create a 3D simulation of how the accident took place and use it to verify or discredit the testimony of individuals involved.
Law enforcement can actually use LiDAR speed guns that allow them to track the speed of passing cars. For citizens, this ensures that there are less tickets that are a result of human error on the officers’ part in determining their speed while allowing law enforcement to do their jobs more efficiently.
Laser scanning in construction
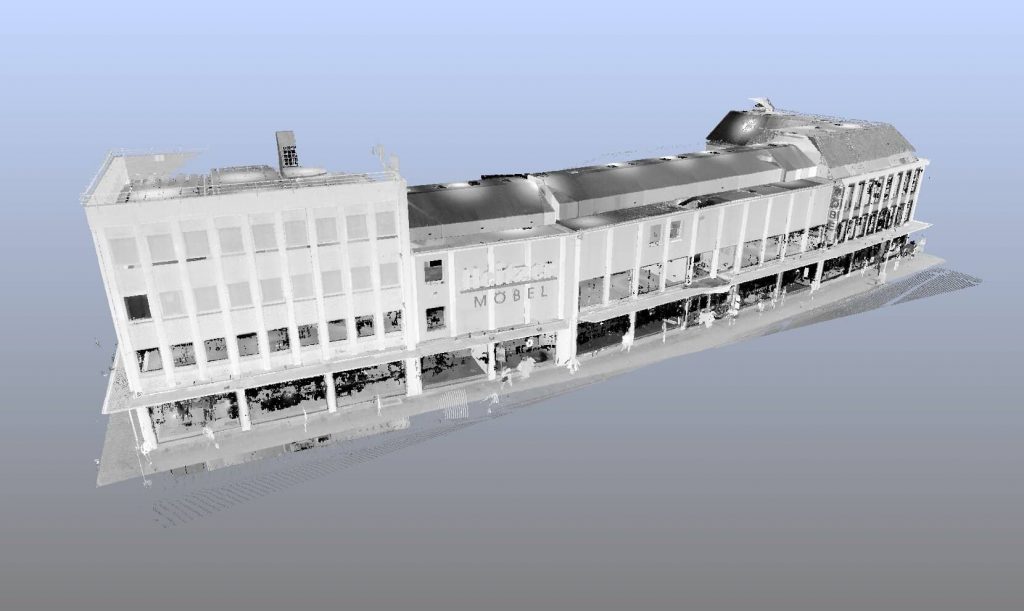

One of the industries most affected by laser scanning is construction. There are seemingly endless ways to apply laser scanning technology to construction. From the creation of blueprints to the discovery of problems. In fact, laser scanning is used during the design, construction and operations phases of the construction process.
Check out our article about “What is 3d laser scanning in construction”
Laser scanning for floor plans
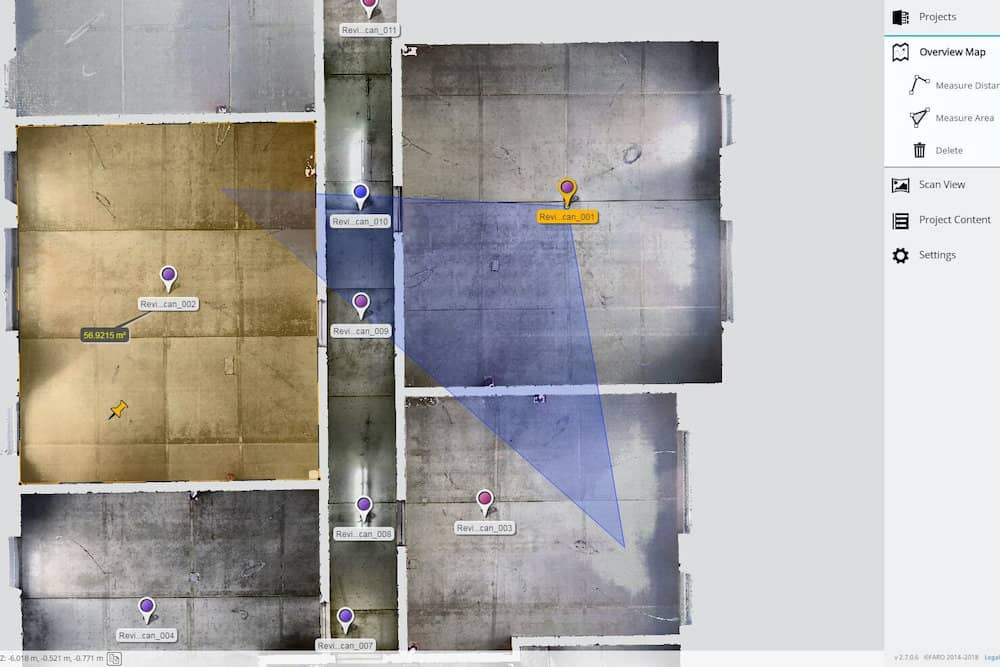

Creating floor plans used to require that you take physical measurements that are prone to human error and time consuming to get. With laser scanning however, the process is much quicker, and the risk of human error is all but removed.
Floor plans are essentially a mapping out of where major structural elements such as doors and windows will go in a room. Often this is done when individuals or businesses are renovating or adding onto their house or building.
The scanners create a 3D model of the room so that you can visualize and plan out where the major structural elements should go more effectively. This cuts out all of the time that would be spent tediously taking all the measurements by hand and them mapping it out by hand.
Laser scanning store fronts and building exteriors
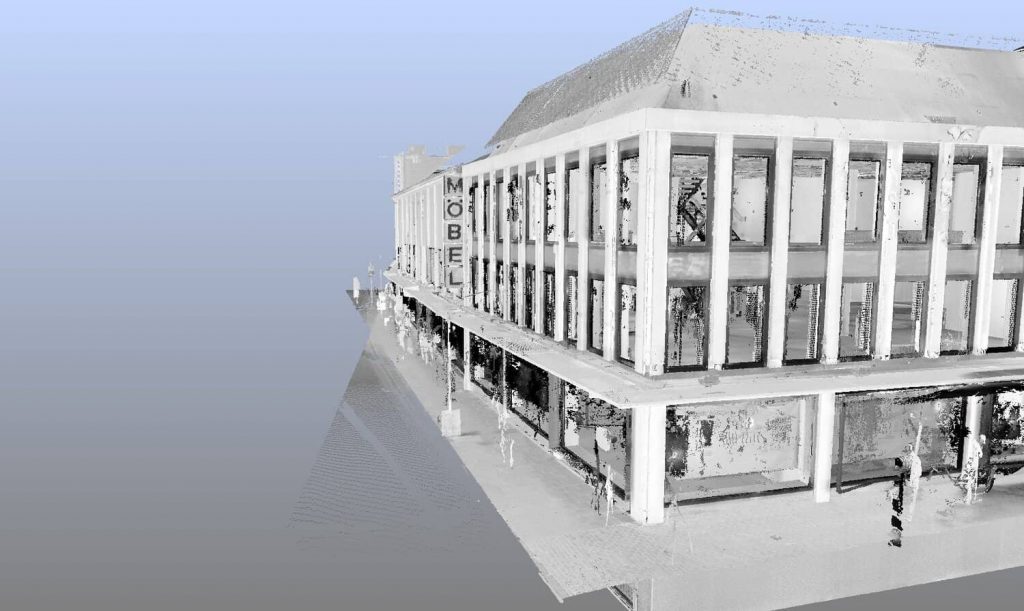

Sometimes laser scanning is used in large scale renovations that include storefronts and building exteriors. The reasons why you would use a laser scanner on the exterior of a building range from simple maintenance to planning construction and can include:
- Planning Structural Elements: Like with interior scans, exterior scans can be used to position outside structural elements like windows and doors as well as the positioning of any special signing that must go up.
- Detecting Deterioration on Building Exteriors: Laser scanners are a relatively inexpensive way to detect any kind of deterioration on a building facade. For example, laser scanning has been used to detect bowing in marble clad building facades.
Laser scanning for interior refurbishments
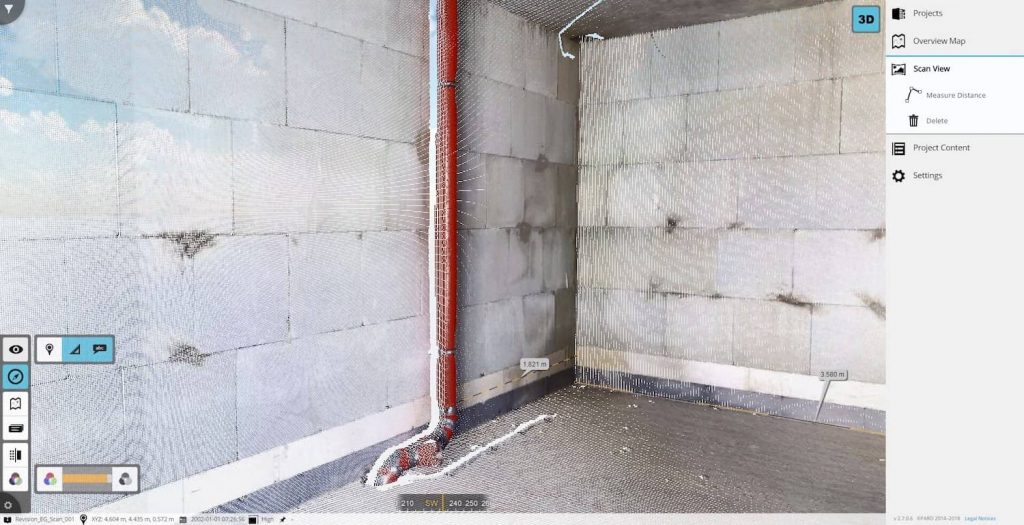

If a scan has been made previously of an interior, it can be used as a reference point during a refurbishment. New scans can be used to create plans for restoration as well as to track progress and ensure everything is going as planned. The biggest benefit is just how accurate a scan is.
In the same way that laser scanning can detect deterioration on building exteriors, it can capture the fine details of an old building that would be much more difficult to spot without it. It can also help you determine what materials may be best to replace those which are damaged, by tracing where the damage is coming from.
Remote measurements anytime with laser scanning
The scans that are conducted get saved onto a cloud for easy access later. If you’re working on a construction project and you need measurements from a place that was previously scanned, you don’t have to physically go back and do another scan. Instead, you can pull up the data remotely anywhere, anytime, and streamline your planning process.
Laser scanning for interior quality control
Laser scanning can be used to ensure that all of the structural elements in an interior design have been placed where they are supposed to be, with the exact dimensions that were planned. It can also save the data it picks up to the cloud for easy retrieval later if any further renovations become necessary.
Laser scanning in robotics
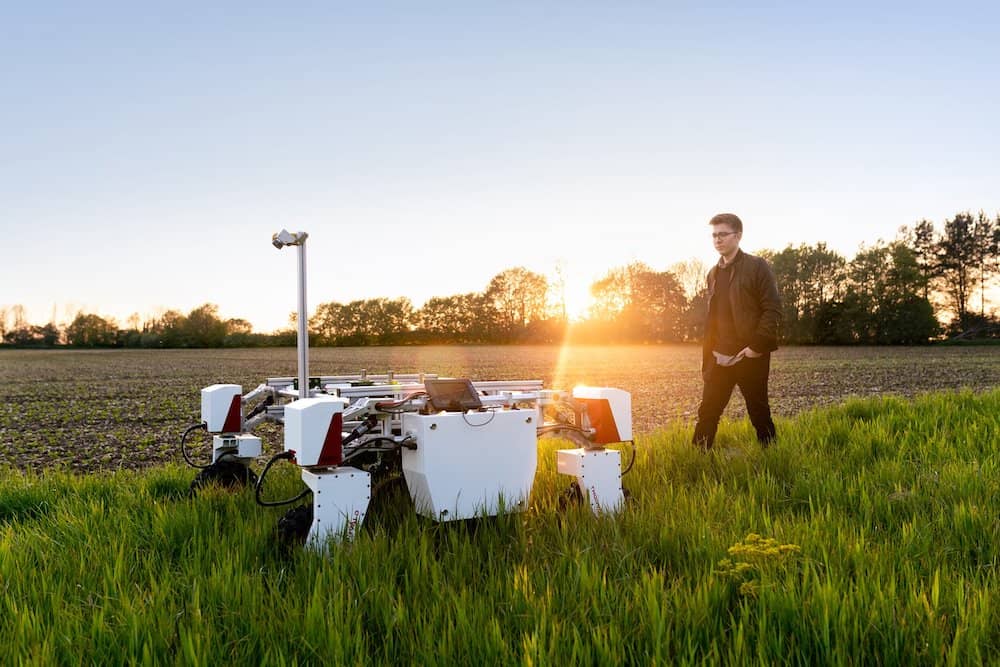

Laser scanning is actually used in robotics to help detect environments and classify objects. When scientists land robotic vehicles, it is a LiDAR system that detects their distance and velocity before landing as well as maps out the terrain. The same laser scanning system is often used in manned vehicles as well.
Laser scanning in the medical field
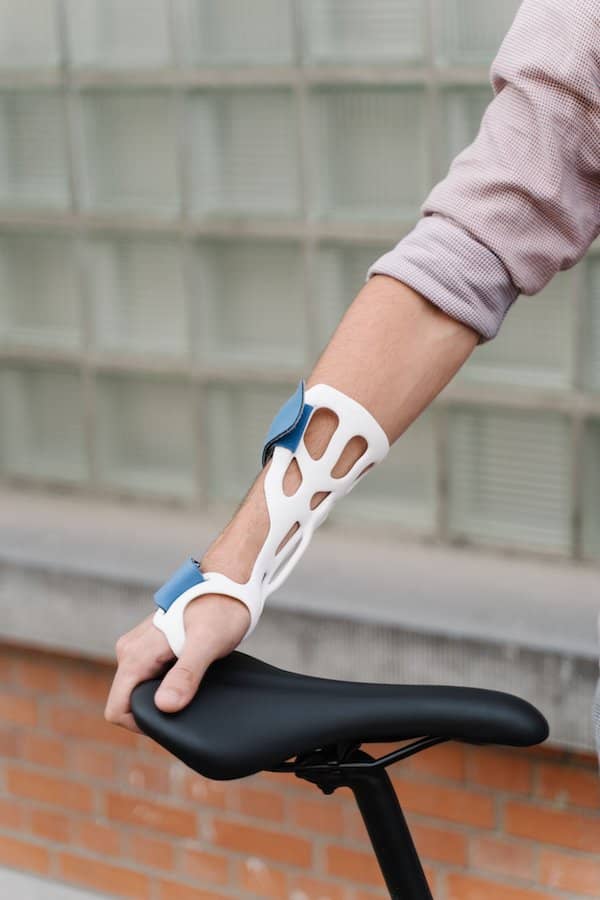
According to a study published in Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, 3D laser scanning is increasingly being used in the medical community as a way to get an accurate measurement “of a patient’s body shape, size and skin surface area or an individual part of the body.”
One practical use for being able to scan the exterior of the body with a laser scanner is that it makes it easier to tailor implants and prosthetics to a patient’s body. For example, if a company needs to manufacture a prosthetic arm for a patient, they can know the exact dimensions they need by accessing the data from a laser scan via the cloud.
The major limitation of laser scanning is that right now, it can only be used to examine the exterior of a body. Fortunately, however, we have other technology such as X Rays to cover the interior while laser scanning advances.
3D facial and body scans through laser scanning
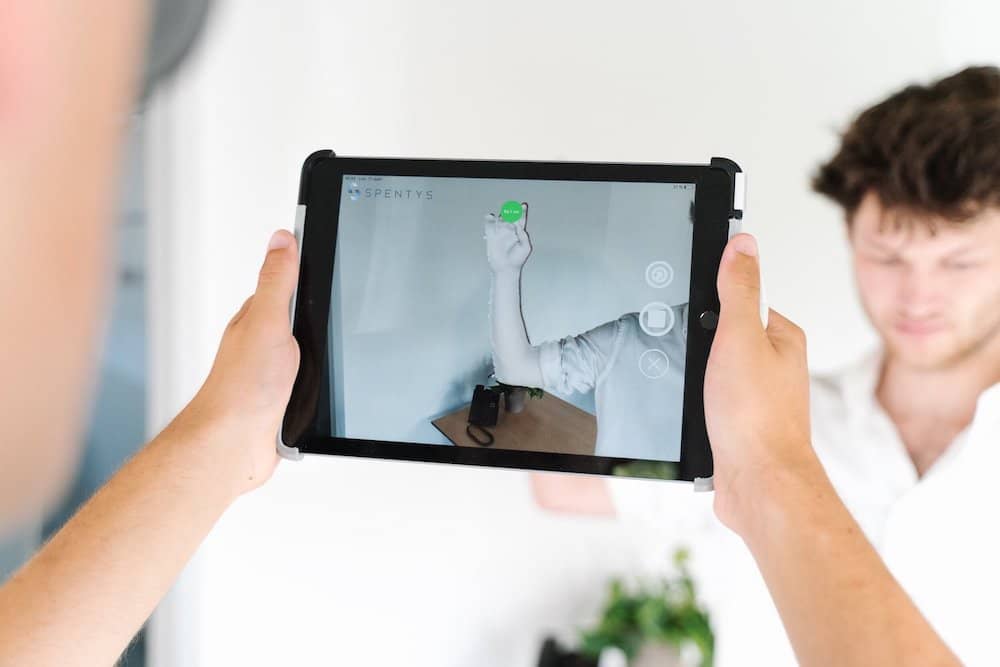

Laser scanning can be used to create complex 3D measurements and models of the human face. The face is one of the hardest parts of the body to accurately measure due to its flexibility and complexity.
Facial scanners take away that difficulty by picking up the entire face all at once in detail. They can actually account for slight movements in the face during a scanning.
It’s important to note here that there are body scanners as well, which can do much the same thing. The body can be very difficult to get an accurate measure of as well.
Both the body and facial scans have applications that range from security to healthcare. In security, these 3D laser scanners have implications on facial recognition software. As for healthcare, when health issues come up related to the face, the doctor can more easily explore the problem and compare the face’s current state to that which is on record.
Laser scanning in forensics & crime scene analysis

With laser scanning, investigators can acquire more evidence in a shorter amount of time than they ever have before. A growing number of law enforcement agencies are using laser scanning to analyze everything from murder scenes to the traffic accidents we mentioned when we brought up laser scanning on the highway. Just a few of the uses of laser scanning in forensics include:
- Preserving a crime scene: With 3D laser scanning a data snapshot of the crime scene and the placement of all the objects within can be quickly uploaded to the cloud and accessed at any time. This helps them to quickly access the crime scene without disturbing it so they more readily begin gathering physical evidence.
- Uncovering a bullet trajectory: In the event of a shooting, investigators can use laser scanning to make a model that simulates the trajectory of a bullet so they can track its origin.
- Blood spatter analysis: Depending on how a victim is attacked, their blood will spatter a certain way. Laser scanners can allow investigators to record the blood spatter and study it more closely, modeling how it would work on the computer.
So, what is laser scanning really used for?
Laser scanning can be used for all kinds of different projects, from manufacturing to cave exploration. Whatever it is being used for, laser scanning is all about measuring distance and creating a 3D model of a given location or object. It is also a powerful tool for organizing data in an easy to access cloud that allows for a holistic approach to surveying.
With laser scanning, you’re not only receiving more accurate results than you would if you manually measured distances, but you’re also massively increasing your efficiency. The combination of perfect measurements, centralized data, and adaptable designs is really what laser scanning is all about. So how will you use laser scanning to make your life easier?
Contact us
Whether you just have a small question or want to get a customized offer from us:
Contact us now.
We are happy to help you.
